Construction site fuel delivery software is transforming how contractors manage their most critical resource, fuel. In an industry where every minute of downtime translates to lost revenue and missed deadlines, implementing efficient on-site fuel delivery management has become a competitive necessity rather than a luxury. This comprehensive playbook explores proven strategies for safe, efficient, and cost-effective construction site refueling operations.
Understanding the Construction Fuel Delivery Landscape
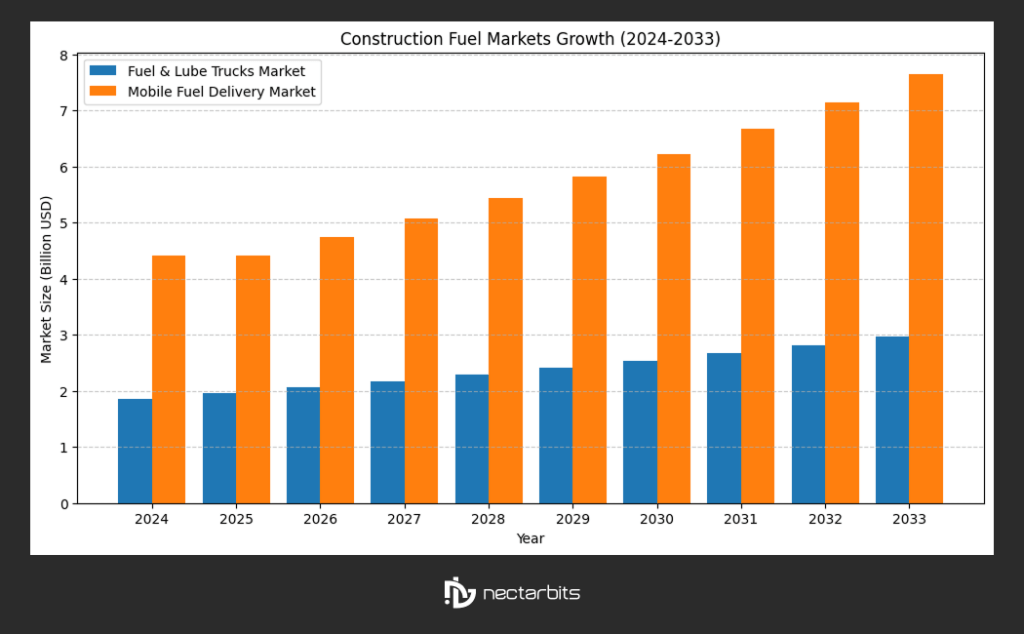
The construction industry operates heavy machinery that consumes significant amounts of diesel fuel daily. According to the global fuel and lube trucks market size, it was estimated at $1.86 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $2.50 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 5.3%. Meanwhile, the mobile fuel delivery market reached $4.42 billion in 2025 and is expected to grow at a 7.1% CAGR through 2033.
These statistics underscore a critical shift in how construction companies approach fuel management. Traditional methods of sending operators off-site for refueling are being replaced by sophisticated fuel management systems for construction operations that minimize downtime and maximize operational efficiency.
The True Cost of Inefficient Fuel Management
Understanding the financial impact of fuel management decisions is crucial for construction project profitability. Industry research reveals that fuel costs can represent 30 to 50 percent or more of equipment operating expenses, making it often the largest and least controlled expense category. According to Fortune Business Insights, construction and infrastructure development was the top application segment in 2024, capturing a 38.5% market share.
When equipment runs out of fuel or requires off-site refueling, the cascading costs extend far beyond the immediate inconvenience. Industry experts concur that unplanned downtime rates between 20 and 30 percent are not uncommon in the construction industry, with each hour of idle equipment representing lost revenue, missed deadlines, and frustrated stakeholders.
Table 1: Financial Impact of Fuel Management Decisions
| Cost Category | Traditional Off-Site Refueling | On-Site Fuel Delivery | Annual Savings Potential |
| Labor Hours Lost | 2-3 hours/day per operator | 0 hours | $15,000-$25,000 |
| Equipment Downtime | 4-6% of operational time | <1% of operational time | $40,000-$60,000 |
| Fuel Waste (Spillage) | 3-5% annual loss | <1% annual loss | $8,000-$12,000 |
| Administrative Overhead | High (manual receipts/tracking) | Low (automated systems) | $10,000-$15,000 |
| Total Annual Savings | — | — | $73,000-$112,000 |
Based on a medium-sized construction operation with 15-20 pieces of heavy equipment
The Strategic Advantages of Construction Site Fuel Delivery Software
Modern fuel delivery for construction sites leverages technology to address the industry’s most pressing challenges. By implementing construction site fuel delivery software, contractors gain unprecedented visibility and control over their fuel operations. Companies like NectarBits, a leading software development company, specialize in creating custom solutions that integrate fuel management with broader operational systems.
Real-Time Inventory Management
Sophisticated fuel management systems for construction operations provide real-time monitoring of fuel levels across all storage tanks and equipment. This proactive approach prevents costly runouts while eliminating unnecessary fuel stockpiling that ties up capital.
Advanced tank monitoring systems send automated alerts when fuel levels reach predetermined thresholds, ensuring timely deliveries without manual intervention. Project managers can access fuel consumption data from any device, enabling data-driven decisions about equipment deployment and fuel ordering.
Enhanced Safety and Compliance
Safety is paramount in construction operations, and fuel handling presents significant risks. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) maintains strict regulations governing fuel storage and handling on construction sites. OSHA regulations require that only designated persons conduct fueling operations, engines must be stopped during refueling, and smoking and open flames are prohibited in fueling areas.
Professional on-site fuel delivery management systems ensure compliance with these regulations while minimizing the risk of accidents, spills, and environmental contamination. Trained fuel delivery professionals handle all aspects of the refueling process, from proper grounding and bonding to spill prevention and containment.
Table 2: OSHA Compliance Requirements for Construction Site Fueling
| Requirement Category | Specific Regulations | Compliance Solutions |
| Container Approval | Only approved containers for flammable liquids; Safety cans for quantities ≤5 gallons | Use certified fuel delivery vehicles; DOT-approved containers |
| Designated Fueling Areas | Equipment refueled only at designated locations; 25-foot separation from other operations | Establish marked fueling zones; Install proper signage |
| Fueling Operations | Engines stopped during refueling; No smoking/open flames within 50 feet | Implement strict protocols; Train all personnel |
| Storage Tank Requirements | Proper labeling with “FLAMMABLE – KEEP FIRE AND FLAME AWAY”; Adequate ventilation | Professional tank installation; Regular inspections |
| Spill Prevention | Drainage systems for spill control; Immediate cleanup procedures | Spill kits on-site; Emergency response plans |
Implementing a Fuel Management System for Construction
Successful implementation of construction site fuel delivery software requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a systematic approach to transitioning from traditional fueling methods to a modern, efficient system.
Step 1: Conduct a Comprehensive Fuel Audit
Begin by analyzing your current fuel consumption patterns, costs, and inefficiencies. Track fuel usage across all equipment for at least 30 days to establish baseline metrics. Document current costs, including direct fuel expenses, labor hours spent refueling, equipment downtime, and administrative overhead.
This audit reveals opportunities for improvement and provides measurable benchmarks for evaluating the impact of your new fuel delivery for construction sites solution.
Step 2: Select the Right Fuel Delivery Partner
Not all fuel delivery services are created equal. When evaluating providers, consider their experience with construction sites, delivery schedule flexibility, fuel quality guarantees, and safety track record. The right partner should offer comprehensive services, including emergency deliveries, fuel quality testing, and regulatory compliance support.
Look for providers who offer integrated technology solutions that connect seamlessly with your existing project management systems. A mobile app development company specializing in construction technology can create custom solutions that bridge gaps between fuel management and broader operational systems.
Step 3: Deploy On-Site Fuel Storage Infrastructure
Proper fuel storage is the foundation of efficient on-site fuel delivery management. Work with your fuel provider to determine optimal tank sizes based on your daily consumption patterns and delivery schedules. Most construction sites benefit from 500-2,000-gallon above-ground storage tanks with appropriate secondary containment systems.
Consider modular tank systems that can be relocated as project phases progress, ensuring fuel remains accessible throughout the construction site lifecycle.
Step 4: Integrate Technology Solutions
Modern fuel delivery for construction sites relies heavily on technology integration. Implement automated tank monitoring systems that transmit real-time fuel level data to both your project management team and your fuel supplier. Many fuel delivery app development solutions offer mobile applications that enable on-site personnel to request deliveries, track consumption, and generate reports from their smartphones.
Integration with telematics systems on your equipment provides even deeper insights, correlating fuel consumption with equipment utilization, operator behavior, and job site productivity metrics.
Step 5: Train Personnel and Establish Protocols
Even the most sophisticated construction site fuel delivery software is only effective if personnel are properly trained. Develop comprehensive training programs covering safety procedures, system operation, emergency response, and regulatory compliance.
Establish clear protocols for routine refueling operations, emergency fuel deliveries, spill response, and tank maintenance. Ensure all personnel understand their roles and responsibilities within the fuel management system for construction operations.

Advanced Strategies for Fuel Delivery for Construction Sites
Once the foundational systems are in place, advanced strategies can further optimize fuel management operations and drive additional value.
Predictive Analytics and Consumption Forecasting
Leverage historical data collected by your fuel management system for construction to develop predictive models that forecast fuel consumption based on project phases, weather conditions, equipment deployment, and operational intensity. These forecasts enable proactive fuel ordering, preventing both runouts and excess inventory.
Advanced analytics can identify consumption anomalies that may indicate equipment problems, fuel theft, or inefficient operating practices, allowing corrective action before minor issues become major problems.
Dynamic Route Optimization for Multi-Site Operations
For contractors managing multiple concurrent projects, coordinating fuel deliveries across sites presents logistical challenges. Modern on-site fuel delivery management systems incorporate route optimization algorithms that consider delivery priorities, traffic conditions, tank levels, and delivery windows to maximize efficiency.
These systems can automatically schedule deliveries to minimize travel time and fuel costs for the delivery fleet while ensuring no construction site experiences fuel shortages.
Integration with Equipment Management Systems
The most sophisticated implementations integrate construction site fuel delivery software with comprehensive equipment management platforms. This integration correlates fuel consumption data with maintenance records, utilization rates, operator assignments, and project costing systems.
Such integration enables holistic equipment performance analysis, revealing relationships between maintenance status, fuel efficiency, operator skill levels, and overall productivity. Contractors can identify opportunities to optimize equipment deployment, target operator training, and make informed equipment acquisition decisions.
Working with an Advanced Logistics & Transport Services Company ensures your fuel management system integrates seamlessly with broader supply chain and logistics operations.
Table 3: Key Performance Indicators for Fuel Management Success
| KPI Category | Metric | Target Benchmark | Measurement Frequency |
| Operational Efficiency | Equipment Downtime Due to Fuel Issues | <0.5% of operating hours | Daily |
| Cost Management | Fuel Cost Per Operating Hour | Industry-specific baseline -10% | Weekly |
| Safety & Compliance | Fuel-Related Safety Incidents | Zero incidents | Monthly |
| Inventory Control | Fuel Runout Events | Zero events | Real-time monitoring |
| Environmental Impact | Fuel Spillage Volume | <0.1% of total delivered | Monthly |
| Supplier Performance | On-Time Delivery Rate | >98% | Weekly |
Safety Protocols and Best Practices
Safety must remain the paramount concern in all fuel delivery for construction site operations. Beyond basic OSHA compliance, implementing comprehensive safety protocols protects personnel, equipment, and the environment.
Pre-Delivery Safety Inspections
Before each fuel delivery, conduct thorough safety inspections of the delivery area. Ensure the delivery path is clear of obstacles, verify that fire extinguishers are accessible and charged, check that all required safety equipment is present and functional, and confirm weather conditions are suitable for safe fuel transfer.
The fuel delivery vehicle itself should undergo pre-trip inspections covering brakes, tires, hoses, nozzles, emergency shut-off systems, and safety equipment. Many construction site fuel delivery software solutions include digital inspection checklists that ensure consistent compliance.
Fuel Transfer Procedures
Proper fuel transfer procedures minimize spill risks and ensure operator safety. Key protocol elements include proper grounding and bonding of delivery equipment to prevent static electricity buildup, verification that engines are shut off during refueling operations, maintaining required clearances from ignition sources, and continuous attendance by trained personnel throughout the transfer process.
Deploy spill containment systems appropriate to the volume being transferred, and maintain spill response equipment in immediately accessible locations.
Emergency Response Planning
Despite rigorous safety protocols, emergencies can occur. Comprehensive emergency response plans address potential scenarios, including fuel spills, fire, equipment malfunction, and personnel injury.
Plans should detail evacuation procedures, emergency contacts, spill containment and cleanup procedures, and coordination with local emergency services. Regular emergency drills ensure personnel can execute response plans effectively under stress.

Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Modern fuel delivery for construction sites increasingly emphasizes environmental stewardship and sustainability. Beyond regulatory compliance, environmental responsibility offers reputational benefits and can reduce long-term operational costs.
Spill Prevention and Containment
Advanced spill prevention strategies include double-walled storage tanks with leak detection systems, automated overfill prevention systems, regular integrity testing of tanks and transfer equipment, and secondary containment systems sized to contain the full volume of the largest tank plus precipitation.
Many construction site fuel delivery software platforms include automated monitoring of containment system integrity, alerting site managers to potential issues before they result in environmental releases.
Emissions Reduction Strategies
Equipment fuel consumption directly correlates with emissions output. Fuel management system for construction operations that optimizes equipment utilization and prevents idling reduce both fuel costs and environmental impact.
Consider implementing policies requiring equipment shutdown during extended idle periods, optimizing equipment sizing for tasks to prevent operating oversized equipment unnecessarily, and scheduling maintenance to ensure engines operate at peak efficiency.
Alternative Fuel Integration
As the construction industry transitions toward lower-carbon operations, fuel management systems must accommodate alternative fuels, including biodiesel blends, renewable diesel, and eventually hydrogen for fuel cell equipment.
Partnering with a Multi-Delivery App Development specialist ensures your fuel management platform can evolve to support diverse fuel types as your equipment fleet modernizes.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Quantifying ROI
Implementing comprehensive on-site fuel delivery management systems requires significant investment. Understanding the return on investment helps justify these expenditures and guides implementation decisions.
Direct Cost Savings
Direct cost savings from construction site fuel delivery software implementation include eliminated labor costs for off-site refueling trips, reduced fuel waste through precise inventory management, lower administrative costs through automated tracking and reporting, and decreased insurance premiums through improved safety records.
For a typical medium-sized construction operation, direct annual savings range from $50,000 to $100,000, with larger operations realizing proportionally greater benefits.
Productivity Improvements
Productivity improvements represent the largest component of ROI from fuel delivery for construction sites optimization. Eliminating equipment downtime due to fuel shortages translates directly to increased revenue generation.
Using conservative estimates, reducing unplanned downtime from 25% to 5% on a $200,000 excavator operating 2,000 hours annually yields productivity gains worth approximately $80,000 per machine annually.
Risk Reduction Value
While difficult to quantify precisely, risk reduction through improved safety and compliance has substantial value. Avoiding a single major fuel spill, fire, or regulatory violation can prevent costs ranging from tens of thousands to millions of dollars in cleanup costs, fines, and litigation expenses.
Insurance carriers increasingly recognize the risk management value of comprehensive fuel management systems, offering premium reductions that further enhance ROI.
To dive deeper into how automation removes delivery chaos,
READ:- our post on automated dispatching software for fuel deliveries.
Case Studies: Real-World Implementation Success
Examining real-world implementations provides practical insights into how construction site fuel delivery software transforms operations.
Case Study 1: Regional Heavy Highway Contractor
A regional heavy highway contractor managing 75 pieces of equipment across 12 active projects implemented comprehensive on-site fuel delivery management across their operations. Before implementation, the company experienced an average of 23% unplanned downtime, with fuel shortages accounting for approximately 15% of downtime events.
After implementing integrated fuel management systems, including automated tank monitoring, predictive ordering, and mobile applications for site personnel, unplanned fuel-related downtime dropped to under 2%. Annual savings exceeded $180,000 from reduced downtime alone, with additional savings from eliminated fuel waste and lower administrative costs.
The implementation paid for itself within 14 months and continues generating positive returns.
Case Study 2: Commercial Building Contractor
A commercial building contractor operating in dense urban environments faced unique challenges with fuel delivery logistics. Traditional fuel delivery to high-rise construction sites involved significant coordination challenges and safety concerns.
By partnering with a fuel supplier offering advanced construction site fuel delivery software with real-time communication capabilities, the contractor established efficient fuel delivery protocols that minimized disruption to surrounding areas and maintained OSHA compliance.
The integrated system reduced average fuel delivery time from 90 minutes to 25 minutes, decreased fuel-related safety incidents to zero over 18 months, and improved project completion rates by eliminating fuel-related delays.
Future Trends in Construction Site Fuel Management
The construction fuel management landscape continues to evolve rapidly. Understanding emerging trends helps contractors prepare for the future and make strategic technology investments.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning technologies are increasingly integrated into fuel management systems for construction platforms. These systems analyze vast datasets to identify patterns invisible to human analysts, predict equipment failures before they occur based on fuel consumption anomalies, optimize delivery scheduling across complex multi-site operations, and automatically adjust fuel ordering based on project schedules, weather forecasts, and historical consumption patterns.
As these technologies mature, they will deliver increasingly sophisticated optimization capabilities.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
IoT sensor technology enables unprecedented visibility into fuel consumption and equipment operations. Modern construction equipment increasingly features built-in telematics that report fuel levels, consumption rates, and operating conditions in real-time.
Integration of IoT sensors with fuel management platforms creates comprehensive digital twins of construction operations, enabling holistic optimization that considers fuel management within the broader context of equipment utilization, project schedules, and resource allocation.
Blockchain for Fuel Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology offers potential for enhanced transparency and traceability throughout the fuel supply chain. Blockchain-based fuel management systems can provide immutable records of fuel deliveries, quality certifications, and consumption, enhanced fraud prevention through transparent transaction records, and automated smart contracts for fuel procurement and payment.
While blockchain adoption in construction fuel management remains nascent, early implementations show promise for addressing supply chain complexity and accountability challenges.
Electrification and Alternative Fuels
As the construction industry transitions toward electrification and alternative fuels, fuel management systems must evolve accordingly. Future on-site fuel delivery management platforms will need to accommodate multiple energy sources, including diesel, biodiesel, renewable diesel, compressed natural gas, hydrogen, and electricity for battery-electric equipment.
This multi-fuel future requires flexible management systems capable of tracking, optimizing, and reporting on diverse energy sources within unified platforms.

Conclusion
The construction industry is entering a new era of fuel management. Traditional reactive practices are giving way to on-site fuel delivery software that optimizes uptime, cost control, safety, compliance, and sustainability.
With fuel and lube truck markets projected to reach $2.50 billion by 2030 and mobile fuel delivery expected to hit $8.75 billion by 2032, technology-driven fuel management is no longer optional; it’s a competitive necessity.
This playbook outlines a practical roadmap for implementing efficient fuel systems at any scale, from fuel audits to predictive analytics. Success depends on leadership commitment, smart technology investments, trusted fuel partners, and continuous optimization—delivering measurable returns in productivity, safety, and profitability.
As construction projects grow more complex, companies with advanced fuel management will lead the market. Now is the time to eliminate inefficiencies, protect margins, and build a stronger competitive advantage.
Related Reading
Curious how a leading B2B fuel delivery platform succeeds in a competitive market? Dive into the Fuel4U blueprint to understand how smart technology, operational efficiency, and enterprise-focused strategy drive scale and profitability.
Read:- the fuel delivery blueprint of Fuel4U in the B2B market to uncover real-world insights behind its success.
FAQs:-
Construction site fuel delivery software is used to monitor fuel levels, automate refueling schedules, reduce equipment downtime, and give project managers real-time visibility into fuel usage across sites and machinery.
Most mid-sized construction companies save tens of thousands annually by reducing idle time, preventing fuel theft, avoiding emergency refueling, and cutting manual fuel tracking and administrative costs.
Yes. By ensuring fuel is available before tanks run empty and predicting consumption patterns, fuel delivery software significantly reduces fuel-related downtime and keeps equipment running as scheduled.
Most modern platforms integrate with equipment telematics, fleet management tools, and project management software, allowing construction teams to manage fuel without changing their existing workflows.








