Quick summary:-
Mobile fuel delivery in the UAE operates under strict regulatory and safety frameworks due to the hazardous nature of fuel transportation.
This guide breaks down key fuel delivery regulations in the UAE, highlights a practical mobile fuel delivery safety checklist, and explains on-demand fuel delivery compliance requirements for businesses targeting global expansion.
Designed for US-based companies, it also shows how technology and compliant fuel delivery apps help meet local laws, reduce risk, and scale operations safely.
Mobile fuel delivery is gaining traction worldwide, but scaling this model depends heavily on meeting strict regulatory standards. For businesses entering the Middle East, fuel delivery regulations in the UAE play a critical role in defining how fuel is transported, stored, and delivered safely. Similar compliance expectations exist in South Africa, where hazardous fuel transport is closely monitored to protect public safety and the environment.
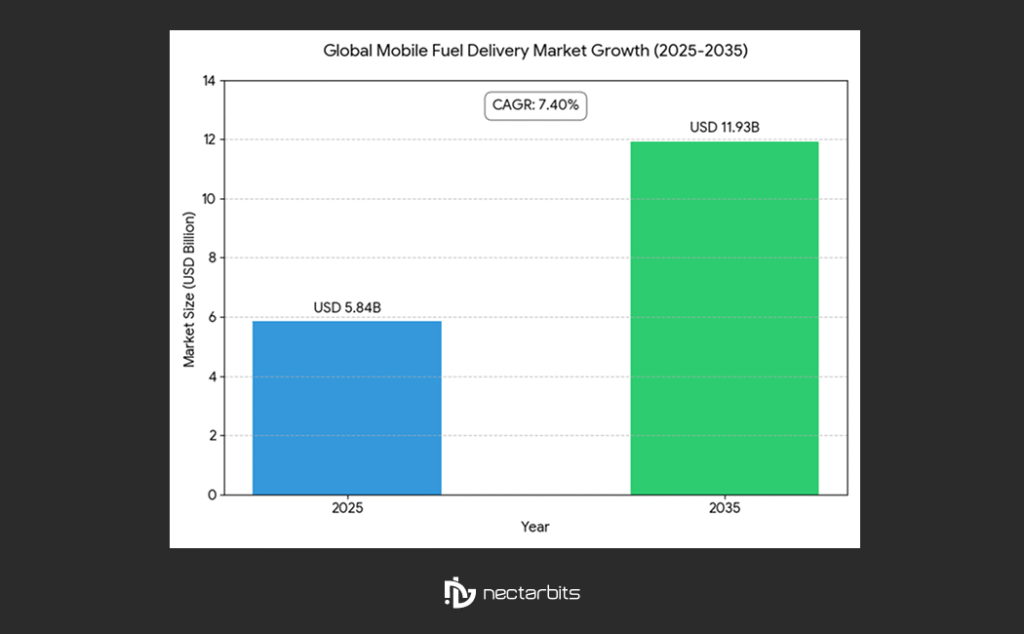
For US-based companies, both regions present strong growth opportunities due to dense commercial fleets, expanding logistics networks, and rising demand for on-demand fueling solutions. The global mobile fuel delivery market is projected to grow from USD 5.84 billion in 2025 to USD 11.93 billion by 2035, underscoring the sector’s momentum and the importance of operating within legal frameworks (source: Future Market Insights).
This guide offers a country-wise, operational, and technology-aligned regulatory and safety checklist to help businesses navigate compliance, reduce risk, and scale mobile fuel delivery operations with confidence.
Why Regulations Matter More in Mobile Fuel Delivery Than Any Other On-Demand Business
Mobile fuel delivery operates in one of the most heavily regulated environments because fuel is classified as a hazardous and flammable commodity. Unlike standard on-demand services, fuel delivery involves high-risk materials that can cause serious safety, environmental, and financial damage if mishandled. As a result, regulatory compliance becomes a core operational requirement rather than a legal formality.
A key distinction lies between traditional fuel stations and mobile fuel delivery models. Fixed fuel stations operate in controlled locations with permanent safety systems, predefined traffic flow, and constant regulatory supervision. Mobile fuel delivery, however, extends fuel handling to fleet yards, construction sites, warehouses, and public roads, dramatically increasing exposure to risk and the need for tighter oversight.
Regulators across global markets focus on several critical risk areas:
- Fire and explosion risks caused by improper handling, faulty equipment, or unsafe delivery environments
- Environmental contamination, including fuel spills that can damage soil and groundwater
- Fuel theft and adulteration, which affect taxation, quality control, and customer trust
- Data tracking and audit trails to ensure every delivery is traceable, verifiable, and compliant
When compared to food delivery or logistics platforms, where risks are primarily operational, mobile fuel delivery combines physical safety, environmental protection, and regulatory accountability in a single workflow. This complexity explains why compliance-driven technology and reliable Fuel Delivery App Development play a crucial role in meeting regulatory expectations and enabling safe, scalable growth.
Global Compliance Framework Every Mobile Fuel Delivery Business Must Follow
Before diving into country-specific regulations in the UAE and South Africa, mobile fuel delivery businesses must establish a global compliance baseline. Fuel delivery operations involve transporting hazardous materials across public and private environments, which places them under international safety, environmental, and operational standards. Most national regulators build their local fuel delivery laws on these globally accepted frameworks.
Core International Standards
Several international standards shape fuel delivery compliance worldwide:
- ADR (Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road):
Sets requirements for hazardous fuel transport, including vehicle specifications, labeling, driver training, and emergency response protocols. - ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 45001:
Focus on quality management, environmental protection, and occupational health and safety, essential for fuel handling, spill prevention, and workforce safety. - NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) Codes:
Widely referenced for fire safety, fuel storage, and dispensing practices, even outside the United States. - UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods:
Provide a global framework for classification, documentation, packaging, and traceability of hazardous materials.
Together, these standards create a foundation for safe operations, environmental accountability, and regulatory transparency.
Technology’s Role in Compliance
Scaling compliance across regions is difficult without digital systems. Regulators increasingly expect:
- GPS tracking and geofencing to control delivery routes and approved zones
- Digital delivery logs for audit-ready documentation
- Fuel quantity verification to prevent theft and discrepancies
- Driver behavior monitoring to reduce safety incidents
Compliance-focused technology ensures these requirements are met consistently and accurately.

Regulatory Checklist for Mobile Fuel Delivery in the UAE
The UAE enforces one of the most structured regulatory environments for fuel handling and transportation in the Middle East. Mobile fuel delivery businesses must comply with federal energy laws, state-level safety regulations, and municipality-specific approvals. This multi-layered framework ensures public safety, environmental protection, and fuel quality integrity.
Key Regulatory Authorities in the UAE
Mobile fuel delivery operations are governed by several key authorities:
- ADNOC (Abu Dhabi National Oil Company): Oversees fuel standards, supply chain controls, and operator approvals.
- Dubai Civil Defence (DCD): Regulates fire safety, hazardous material handling, and emergency preparedness.
- Ministry of Energy & Infrastructure: Sets national fuel transport and energy policies.
- Emirates Authority for Standardization & Metrology (ESMA): Defines equipment, tanker, and fuel quality standards.
- Local Municipalities: Issue operational NOCs and site-specific permissions.
Each authority plays a role in licensing, inspections, and ongoing compliance monitoring.
Licensing & Registration
Businesses need multiple approvals to operate legally:
| Requirement | Purpose |
| Commercial trade license | Legal operation of business |
| Fuel distribution permit | Authorized fuel handling |
| Hazardous material transport license | Compliance for transport |
| Municipality NOCs | Local operational approval |
| Driver certifications | Safety and hazard handling |
Vehicle & Equipment Safety
- Certified tanker specifications
- Anti-spill valves and flame arrestors
- Emergency shutoff systems
- Proper hazard signage and branding
Driver & Staff Safety
- ADNOC-approved training and certifications
- Fire safety and PPE compliance
- Fatigue management policies
Environmental & Spill Management
- Spill response kits on every vehicle
- Waste disposal protocols and soil protection
- Mandatory incident reporting
Digital Compliance
- GPS tracking and geofencing
- Real-time digital delivery logs
- Audit-ready reporting systems, integrated with ERP or fleet software
Using a mobile fuel delivery app helps streamline compliance, track deliveries, and maintain audit-ready documentation.
Regulatory Checklist for Mobile Fuel Delivery in South Africa
South Africa emphasizes occupational safety, environmental protection, and fuel integrity. Compliance is multi-layered due to commercial logistics and mining operations.
Governing Bodies
- DMRE (Department of Mineral Resources & Energy)
- SABS (South African Bureau of Standards)
- NRCS (National Regulator for Compulsory Specifications)
- Department of Transport
- Environmental Affairs
Licensing & Legal Requirements
| Requirement | Purpose |
| Wholesale petroleum license | Legal fuel sale and distribution |
| Dangerous goods transport permit | Hazardous fuel transport |
| Local zoning approvals | Operational permission |
| Cross-border transport compliance | Legal for international transport |
Fuel Transport & Storage
- Certified tankers (SANS standards)
- Regular vehicle inspections and load limits
- Anti-theft and sealing mechanisms
Driver Training & Safety
- Hazmat certifications
- Compliance with the Occupational Health & Safety Act
- Incident reporting procedures
- Alcohol and drug testing policies
Environmental Compliance
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA)
- Spill response and containment
- Emission control and waste handling
Data, Audits & Record-Keeping
- Long-term delivery documentation retention
- Digital invoicing and traceability
- Regulatory audits require end-to-end reporting
According to Transport World Africa, over 70% of commercial freight relies on regulated fuel logistics (Transport World Africa).
Technology Checklist to Stay Compliant in Both the UAE & South Africa
Scaling mobile fuel delivery operations across regions like the UAE and South Africa requires more than understanding regulations; it demands technology-driven compliance solutions. Manual record-keeping and ad hoc checks often fail to meet the stringent safety and reporting standards regulators expect, especially when fleets grow or operate as an on-demand fuel delivery service.
Must-Have Features in a Fuel Delivery App
A robust mobile fuel delivery app is central to meeting regulatory requirements and streamlining operations. Key features include:
- Real-time GPS tracking: Monitor vehicle locations and approved delivery zones to ensure regulatory compliance and optimize routing.
- Driver authentication: Confirm that only certified personnel handle hazardous fuel deliveries.
- Digital delivery proof: Capture electronic signatures, photos, and timestamps for every transaction, creating an audit-ready record.
- Fuel quantity verification: Track exact volumes loaded and delivered, reducing risk of theft, spillage, or audit disputes.
- Automated compliance reports: Generate standardized reports for regulators, internal audits, and fleet managers with minimal manual input.
Why Manual Compliance Fails at Scale
Relying on paper logs, spreadsheets, or verbal confirmations introduces multiple risks:
- Human error: Manual recording can lead to misreported deliveries, missing data, or incorrect quantities.
- Audit delays: Inspectors often require digital proof of compliance; manual systems slow approvals.
- Data tampering risks: Paper-based logs or fragmented digital systems can be altered, creating regulatory liabilities.
By integrating these capabilities, businesses can proactively meet international and local regulatory standards, reduce operational risks, and improve efficiency. A technology-first approach also enables fleet managers to focus on growth and customer satisfaction instead of chasing compliance issues.
Common Compliance Mistakes That Shut Down Fuel Delivery Startups
Even with strong market demand, many mobile fuel delivery startups fail due to preventable compliance oversights. Here are the most common mistakes that can halt operations:
- Operating Without Municipal Clearance
Local authorities require site-specific approvals and No Objection Certificates (NOCs). Skipping this step can result in fines, license suspension, or permanent bans. - Using Non-Certified Tankers or Equipment
Vehicles must comply with national safety standards, including anti-spill valves, flame arrestors, and emergency shutoff systems. Non-compliant equipment increases the risk of accidents, insurance denial, and regulatory penalties. - Relying on Manual Fuel Logs
Paper-based tracking leads to human errors, delayed audits, and inaccurate reporting. This makes it difficult to prove compliance during inspections. - Ignoring Driver Training and Certifications
Drivers must complete hazard material training, fire safety certification, and PPE compliance programs. Neglecting training exposes the business to safety hazards and regulatory fines. - No Emergency Response Plan
Without a proper plan for spills, fires, or accidents, startups remain vulnerable to operational shutdowns and reputational damage.
Pro Tip: Implementing a mobile fuel delivery app can automate logs, track driver activity, verify deliveries, and generate audit-ready reports, mitigating most of these common risks.
For a deeper dive into fuel delivery safety and building customer trust,
Read our comprehensive guide on fuel delivery app safety and compliance
Preparing Your Fleet for International Fuel Delivery Compliance
Expanding mobile fuel delivery operations into international markets like the UAE and South Africa presents a critical compliance challenge: regulatory landscapes differ significantly from one country to another. While the United States has well‑established hazardous material transport frameworks, emerging markets often combine federal, emirate, provincial, and municipal requirements that can be difficult to decode without proper preparation. According to market forecasts, the global mobile fuel delivery market is expected to grow from USD 5.84 billion in 2025 to USD 11.93 billion by 2035, showing the rising importance of establishing compliant international operations. (Source: business research insights)
A key success factor is building strong local partnerships. Regional operators, safety consultants, and legal advisors provide insights into licensing approvals, site‑specific safety standards, and municipal permits, helping you avoid costly delays or penalties. Their expertise becomes invaluable when navigating local customs, documentation norms, and inspection regimes.
Technology is another cornerstone of international compliance. Adapting your systems to support multi‑country compliance, such as tracking driver certifications, recording GPS routes, verifying fuel quantities, and generating audit‑ready reports, reduces risk and enhances transparency. Digital systems also allow for consistent enforcement of best practices, even as your fleet scales across borders.
Ultimately, the most successful global fuel delivery operations are those that prioritize compliance from day one, combining technology, local expertise, and standardized workflows to maintain safety, legal adherence, and operational efficiency.

How Nectarbits Helps Build Regulation-Ready Fuel Delivery Platforms
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape of mobile fuel delivery requires more than basic app functionality; it demands a compliance-first, technology-driven approach. Nectarbits specializes in helping businesses develop platforms that are regulation-ready, scalable, and secure, enabling smooth operations across multiple markets, including the UAE and South Africa.
Our custom fuel delivery app development services focus on key areas that ensure both operational efficiency and regulatory adherence:
- Compliance-First Architecture: Systems are designed to meet international and local regulations from day one, reducing the risk of violations and shutdowns.
- Country-Specific Feature Customization: Apps are tailored to handle local licensing, hazardous material handling, municipal approvals, and environmental requirements.
- Audit-Ready Reporting Systems: Every transaction, delivery, and driver activity is tracked digitally to create a transparent, verifiable audit trail.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Robust security measures protect sensitive data, fuel transaction logs, and fleet information against breaches or tampering.
By leveraging custom software development services, Nectarbits ensures your mobile fuel delivery platform is not only functional but also compliant, safe, and scalable. This allows fleet managers to focus on growth and customer service rather than worrying about regulatory risks.
Conclusion
Compliance is no longer optional; it’s a growth strategy for mobile fuel delivery businesses. Ignoring regulations can quickly lead to operational shutdowns, fines, and reputational damage. Conversely, understanding and implementing fuel delivery regulations in the UAE and South Africa opens doors to highly lucrative markets with dense fleets, energy hubs, and growing logistics demand.
The key to success lies in the intersection of technology and regulation. A well-designed platform that integrates GPS tracking, digital delivery logs, driver authentication, and automated compliance reporting ensures safe, audit-ready operations. By building compliance-first solutions from day one, businesses can scale confidently across borders, minimize risk, and optimize operational efficiency.
For companies looking to capitalize on international opportunities, starting with a robust, regulation-ready platform is critical. Leveraging technology not only simplifies compliance but also enhances customer trust, safety, and overall fleet performance.
Start building your compliant fuel delivery platform today and turn regulatory adherence into a competitive advantage.
Related Reads: Learn from Global Compliance
Studying international fuel delivery regulations can help shape safer and more efficient local practices. Key lessons from the US and Canada, covering licensing, driver certifications, and digital reporting, can be adapted for markets like the UAE and South Africa.
Learning from global standards not only ensures compliance but also builds trust with regulators and customers.
Explore how cross-border fuel delivery regulations work in the US and Canada
FAQs:
In the UAE, fuel delivery requires company licensing, operator permits, and HSE compliance per ENOC or ADNOC standards. Vehicle licenses, driver certifications, Dangerous Goods Regulations adherence, and emergency response plans are mandatory. Ensure proper fuel-type labeling, incident reporting, and periodic audits by regulatory authorities, including incident investigations and corrective tracking.
UAE safety standards require adherence to the UAE Fire and Life Safety Code, GCC Dangerous Goods, and ADNOC/ENOC guidelines. Implement risk assessments, PPE, spill containment, grounding, bonding, and leak detection. Regular training, drills, incident reporting, and third-party audits ensure ongoing compliance with fuel transfer, storage, and transport operations across facilities nationwide.
South Africa enforces fuel delivery safety through the Occupational Health and Safety Act, NFPA-based fire systems, SABS standards, and hazardous substance regulations. Requirements include risk assessments, licensed drivers, vehicle safety standards, anti-spill measures, emergency response plans, and reporting to the Department of Employment and Labour and the Department of Mineral Resources.
Both regions require driver qualifications, but standards differ. UAE mandates trained, licensed drivers with Dangerous Goods endorsement and vehicle-specific certifications. South Africa requires professional driver licenses, fit-for-purpose training, and compliance with hazardous materials transport rules. Regular competency assessments and refresher courses are encouraged to maintain ongoing regulatory alignment across industries.
Penalties include fines, license suspensions, and possible business shutdowns. UAE focuses on regulatory fines, operator sanctions, and enforcement actions for safety violations. South Africa imposes penalties under the OHS Act, environmental fines, and transport regulations; repeat offenses can trigger audits, stricter oversight, and criminal charges in severe cases against offending entities.








