The digital transformation of grocery shopping has fundamentally reshaped how Americans purchase their daily essentials, with the Instacart business model leading this revolutionary change. As the premier on-demand grocery delivery platform in North America, the Instacart business model has evolved from a simple delivery service into a comprehensive multi-sided marketplace that connects millions of consumers with thousands of retailers through an innovative technology-driven platform.
The Evolution of On-Demand Delivery in the U.S.
The on-demand delivery ecosystem in the United States has undergone a dramatic transformation over the past decade, fundamentally altering consumer expectations around convenience, speed, and accessibility. The U.S. online grocery market has grown from a $1.2 billion industry in 2013 to over $95 billion in 2024, representing a compound annual growth rate exceeding 40%.
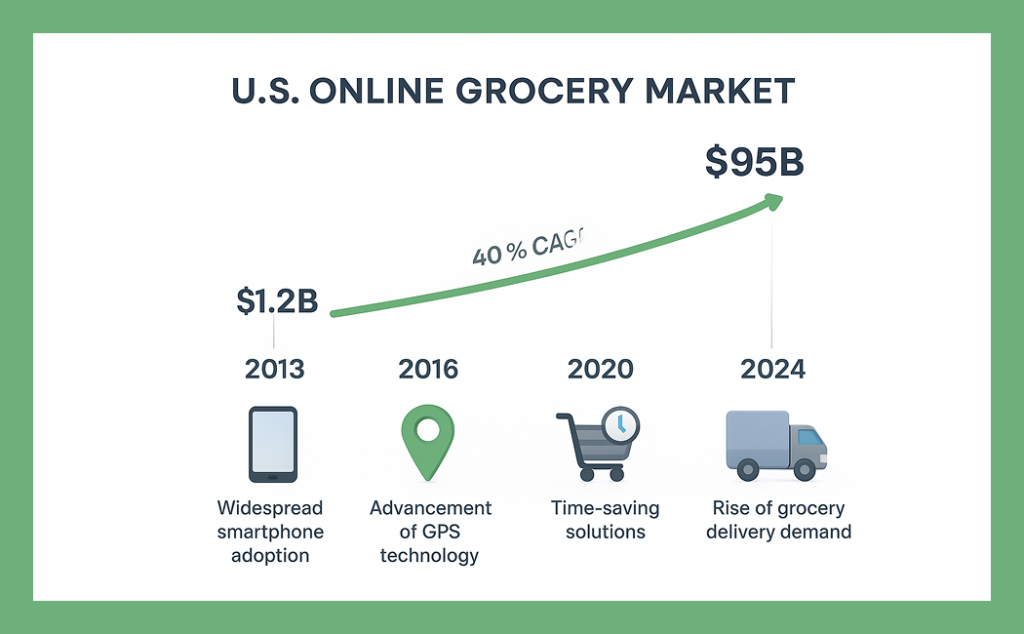
This growth trajectory reflects several key trends:
- Modern consumers increasingly prioritise time-saving solutions
- 67% of shoppers express a desire for grocery delivery or pickup options
- Technological infrastructure has matured with widespread smartphone adoption and sophisticated GPS technology
Instacart’s Rise to Market Leadership
Founded in 2012 by Apoorva Mehta, Max Mullen, and Brandon Leonardo, Instacart emerged during the early wave of on-demand services. The Instacart business model strategic evolution involved several key phases:
Phase 1: Market Validation (2012-2015). Initially launching in San Francisco, the Instacart business model focused on proving viability through partnerships with premium retailers like Whole Foods.
Phase 2: Geographic Expansion (2015-2018) Rapid expansion across major metropolitan markets, establishing partnerships with national chains like Safeway, Kroger, and Costco.
Phase 3: Platform Diversification (2018-2021) Evolution beyond pure grocery delivery, the Instacart business model added alcohol delivery, pharmacy services, big-box retail partnerships, and advertising offerings.
Phase 4: Market Dominance and Profitability (2021-Present) The Instacart business model focuses on optimising margins, enhancing technology capabilities, and expanding through vertical integration.
This strategic evolution has driven the company’s revenue over the last twelve months to $3.46 billion, representing an 11.34% year-over-year increase, demonstrating how the Instacart business model successfully transitioned from a growth-focused startup to a profitable, mature platform business.
Understanding Instacart: The Core Business
What Is Instacart? A Multi-Sided Platform
At its core, the Instacart business model operates as a sophisticated multi-sided platform that creates value by facilitating transactions between three distinct stakeholder groups:
- Consumers seeking convenient grocery shopping
- Personal shoppers looking for flexible income opportunities
- Retailers wanting to expand their digital presence without significant infrastructure investment
The Instacart business model generates value through network effects, where the platform becomes more valuable to each user group as the number of participants in other groups increases.
The Three Pillars: Customers, Shoppers, and Retail Partners
Customers: The Demand Side Instacart serves over 5.5 million active customers across the United States and Canada. The customer value proposition includes:
- Convenience through multi-store shopping in a single transaction
- Time savings by eliminating travel and in-store navigation
- Extensive product selection from hundreds of thousands of stores
- Flexible scheduling options, including same-day delivery
Personal Shoppers: The Supply Side Over 600,000 independent contractors provide the human element crucial to grocery delivery success. Shoppers benefit from:
- Complete scheduling flexibility without fixed schedules
- Competitive compensation ranging from $15-25+ per hour
- Low barriers to entry beyond age, vehicle access, and background checks
- Valuable skill development opportunities in customer service
Retail Partners: The Infrastructure Foundation Instacart partners with over 85,000 stores across 14,000+ cities, ranging from national chains like Kroger and Costco to independent local grocers. These partnerships provide:
- Turnkey technology platforms
- Immediate market presence without internal development
- Incremental revenue through new customer acquisition
- Valuable data and analytics intelligence
For businesses exploring comprehensive solutions, partnering with experienced developers who understand the complexities of multi-sided marketplace dynamics can significantly accelerate time-to-market. Whether you need a full-featured grocery delivery app development platform or specialised solutions for niche markets, the key is choosing partners who have demonstrated success in building scalable, technology-driven platforms that can compete with established players.
The Instacart Business Model & Revenue Model
How Instacart Makes Money: A Diversified Revenue Engine
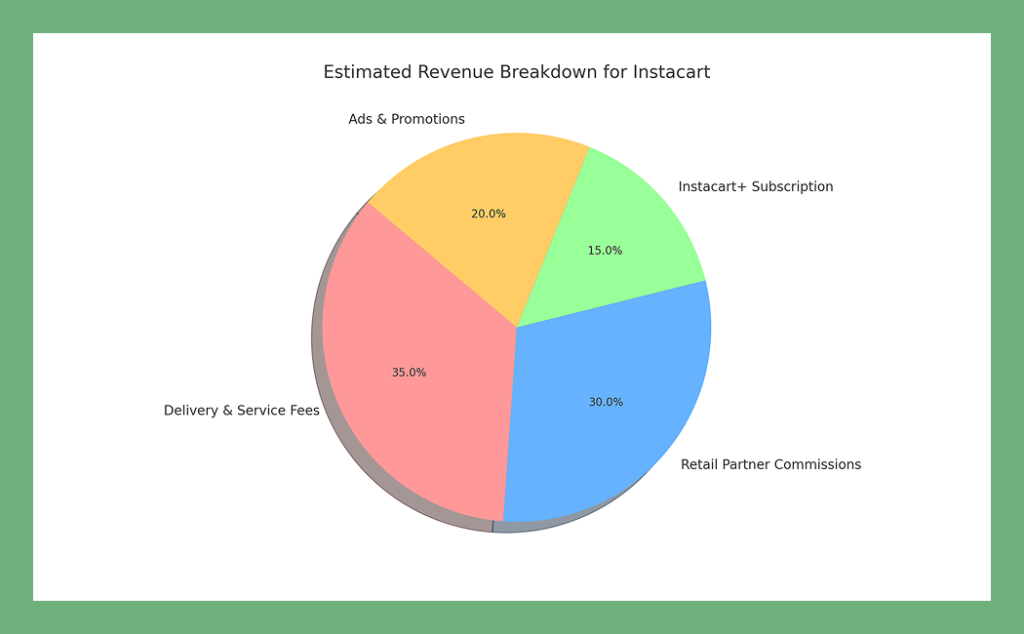
The instacart business model generates income through multiple sophisticated revenue streams that work synergistically to create sustainable profitability:
1. Fees from Customers
- Delivery Fees: $3.99-$5.99 for standard delivery, $5.99-$9.99 for fast delivery
- Service Fees: Typically 5-10% of order value, covering operational costs
- Dynamic Surge Pricing: 1.2x to 3.0x multipliers during peak demand periods
2. Commissions from Retail Partners Standard commissions typically range from 3-15% of gross merchandise value, with volume-based tiers and category-specific rates. Beyond basic commissions, the instacart business model generates additional revenue through:
- Catalog management fees
- Analytics and insights services
- Marketing campaigns
- Technology integration services
3. Instacart+ Subscription Program Priced at $99 per year, providing:
- Free delivery on orders over $35
- Reduced service fees
- Priority access during high-demand periods
- Exclusive offers and family sharing capabilities
Subscription members order 2.5x more than non-members and show 40% greater lifetime value.
4. Instacart Ads & Promotions: The High-Margin Advertising Powerhouse Advertising revenue reached $246 million, up 11% year over year, representing the highest-margin revenue stream. The platform features:
- Sponsored products with pay-per-click pricing
- Display advertising priced on CPM basis
- Advanced targeting through behavioral, geographic, and demographic data
- Cross-category analysis for bundle promotions
Technology, Operations, and Competitive Edge
The Technology Ecosystem
Instacart’s success relies on sophisticated cloud-native architecture designed to handle millions of simultaneous users. Key technological components include:
- Microservices architecture enabling independent scaling
- Real-time data processing handling millions of inventory updates per second
- Mobile-first applications with cross-platform consistency
- AI-powered logistics for order batching and delivery routing
Strategic Advantages & Reasons for Success
First-Mover Advantage and Network Effects The instacart business model benefits from early market entry that provided:
- Brand recognition synonymous with grocery delivery
- Prime partnership access with premium retailers
- Technology head start through years of platform development
- Extensive data accumulation providing AI training advantages
Network effects create exponential value: more consumers attract more shoppers, while more shoppers enable faster delivery times, attracting more consumers. Similarly, more retailers provide greater selection, attracting consumers, while larger consumer bases attract retailers.
Strategic Alliances with Major Retail Chains Strategic retailer relationships provide competitive moats for the instacart business model through:
- Exclusive partnerships like Costco preventing competitor access
- Regional chain partnerships providing local market dominance
- Deep API-level integration enabling real-time inventory synchronization
- White-label solutions creating switching costs
Challenges and The Competitive Arena
Key Challenges Facing the Instacart Business Model
The Economics of Delivery: Navigating Thin Profit Margins The instacart business model operates on fundamentally challenging economics due to low-margin products and high fulfillment costs. The cost structure includes:
- Shopper compensation: $8-15 per delivery
- Customer acquisition costs: $25-50 per new customer
- Technology infrastructure: $2-3 per order
- Payment processing fees: 2.5-3% of order value
Labor Model Complexities The instacart business model depends on classifying shoppers as independent contractors, creating ongoing regulatory challenges with evolving state and federal regulations, benefits pressure, and complex performance management requirements.
The Competitive Landscape
Direct Rivals
- DoorDash: Leveraging existing driver networks and restaurant delivery infrastructure
- Uber Eats: Global scale and integrated rideshare ecosystem
- Target-owned Shipt: Deep integration with Target stores and regional concentration
The Behemoths: Amazon Fresh and Walmart Delivery Amazon Fresh represents the most significant competitive threat through Prime integration, world-class fulfillment infrastructure, and unlimited financial resources. Walmart challenges through 4,700+ U.S. store locations, supply chain integration, and everyday low pricing strategy.
The Future of Instacart
Innovating Beyond Delivery: Instacart’s Next Chapter
Enterprise Technology Solutions Through the Caper AI acquisition, Instacart is developing in-store technology solutions featuring:
- Automatic item recognition through computer vision
- Real-time price displays and integrated contactless payment
- Comprehensive fulfillment services including white-label e-commerce platforms
- Micro-fulfillment centers with robotics integration
Expansion into New Verticals
- Healthcare: Prescription delivery services through pharmacy partnerships, improving medication adherence and accessibility
- Big-Box Retail: Electronics through Best Buy partnerships, home improvement categories, and specialty retail expansion
The expansion model pioneered by Instacart demonstrates the potential for diversification beyond traditional grocery categories. Similar expansion opportunities exist across various industries, from specialised delivery services like fuel delivery solutions to comprehensive marketplace platforms. The key is identifying markets with similar characteristics: high frequency, essential demand, and significant friction in traditional fulfilment models.
The Role of AI in Hyper-Personalised Shopping
Next-generation AI capabilities transform shopping experiences through:
- Predictive shopping lists analysing consumption patterns
- Visual recognition technology enabling image-based search
- Conversational commerce through natural language processing
- Dynamic pricing and promotion optimisation based on purchase history
Strategic Insights and Industry Implications
Instacart as a Blueprint for Modern E-commerce Logistics
The Instacart business model evolution demonstrates key principles foundational for digital commerce:
- Platform Business Model Supremacy: Network effects create sustainable competitive advantages
- Asset-Light Scalability: Rapid geographic expansion without capital intensity
- Technology-Driven Differentiation: Continuous AI investment creates competitive moats
- Diversified Revenue Optimization: Multiple monetization strategies reduce dependency risks
- Stakeholder Alignment: Creating genuine value for all participants ensures sustainable growth
Future Outlook: Maintaining Dominance Through Innovation
The Instacart business model enters 2025 with sustainable advantages including market leadership, technology moats, deep retailer relationships, and diversified revenue streams. However, strategic challenges include big tech competition, labor model vulnerability, market saturation, and potential technology disruption.
The path to continued dominance depends on:
- Innovation leadership through AI and automation investment
- Geographic expansion into underserved markets
- Vertical integration into adjacent services
- Strategic partnership deepening
- Operational excellence optimization
Conclusion
The Instacart business model has fundamentally transformed the grocery industry, establishing a blueprint for successful on-demand delivery platforms through diversified revenue streams, strategic partnerships, and technology innovation. The company’s evolution from simple delivery service to comprehensive marketplace demonstrates that sustainable success requires understanding multi-sided marketplace dynamics, operational excellence, and stakeholder value creation. For businesses exploring grocery delivery solutions, the Instacart business model proves that competitive advantage comes not just from technology, but from creating genuine value for consumers, shoppers, and retailers while maintaining constant innovation and strategic agility in the evolving digital commerce landscape.
Whether developing internal capabilities or working with development partners, businesses must recognise that creating successful grocery delivery platforms requires more than technology it demands a deep understanding of multi-sided marketplace dynamics, stakeholder value creation, and operational excellence necessary to deliver consistent, high-quality service at scale. Instacart’s business model demonstrates that success in the grocery delivery industry requires balancing technological innovation with operational efficiency, customer satisfaction with profitability, and growth ambitions with sustainable business practices.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A: The cost typically ranges from $50,000 to $300,000+, depending on features, complexity, and platform requirements. Basic MVP versions start around $50K-$80K, while full-featured platforms with advanced AI and multi-platform support can exceed $200K-$300K.
A: Development timelines vary from 4-12 months. An MVP can be built in 4-6 months, while a comprehensive platform with advanced features typically takes 8-12 months, including testing and deployment.
A: Essential features include user registration, store browsing, cart management, real-time order tracking, multiple payment options, shopper assignment, in-app messaging, rating systems, and an admin dashboard for management.
A: Yes, we build API integrations with retailer POS systems for real-time inventory updates, ensuring accurate product availability and pricing information for customers.
A: We recommend developing for iOS, Android, and web platforms simultaneously. Most successful apps launch with native mobile apps and responsive web applications to maximize market reach.








