Choosing between a mobile apps v a web apps depends on your goals. Mobile apps deliver interactive experiences, and frequent engagement, utilising device-specific features like GPS and cameras. Web apps, however, are ideal for broad accessibility and consistent performance across devices without requiring downloads.
Native apps lead the way in development with superior performance, seamless user experiences, and full use of device capabilities. Unlike hybrid approaches, native development avoids compromises in quality and functionality, ensuring a robust and high-quality solution.
With more than 6.3 billion smartphone users worldwide, mobile apps offer exponential growth opportunities to app publishers.
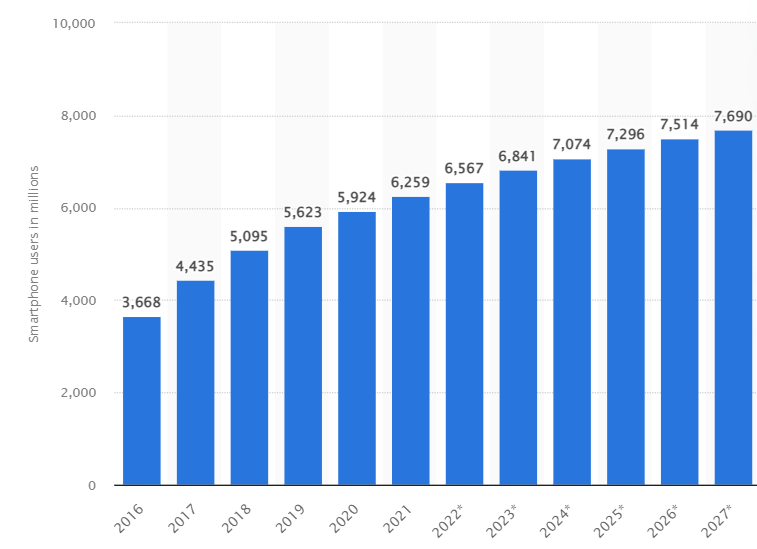
Source: Statista
In fact, the overall mobile app market is projected to generate a staggering $613 billion in revenue by 2025.
Evaluate your audience, functionality needs, and business objectives to make the right choice and achieve optimal results.
Understanding the Development Approaches
1. Native App Development
It involves building an app for a particular operating system like- Android and iOS, where distinct programming languages Java or Kotlin, and Swift or Objective C are used. Various native tools, libraries, and resources are provided by both Google and Apple to create best-in-class native apps. The users can access the iOS and Android mobile app development from different app stores- Apple Store and Google Play store.
2. Hybrid App Development
A cross-platform approach is used to develop apps that work on both Android and iOS. These apps leverage HTML, CSS, and JS and are then wrapped in native environments. Available on app stores, hybrid apps can partially leverage device hardware features while offering cost and time efficiency.
3. Web App Development
Platform-independent apps that run directly in a browser, without the need for downloading. Users can access web apps With a stable internet connection and the app’s URL. They offer excellent UI/UX across devices without consuming device storage. Web app development is thus truly one-of-a-kind and future-proof.
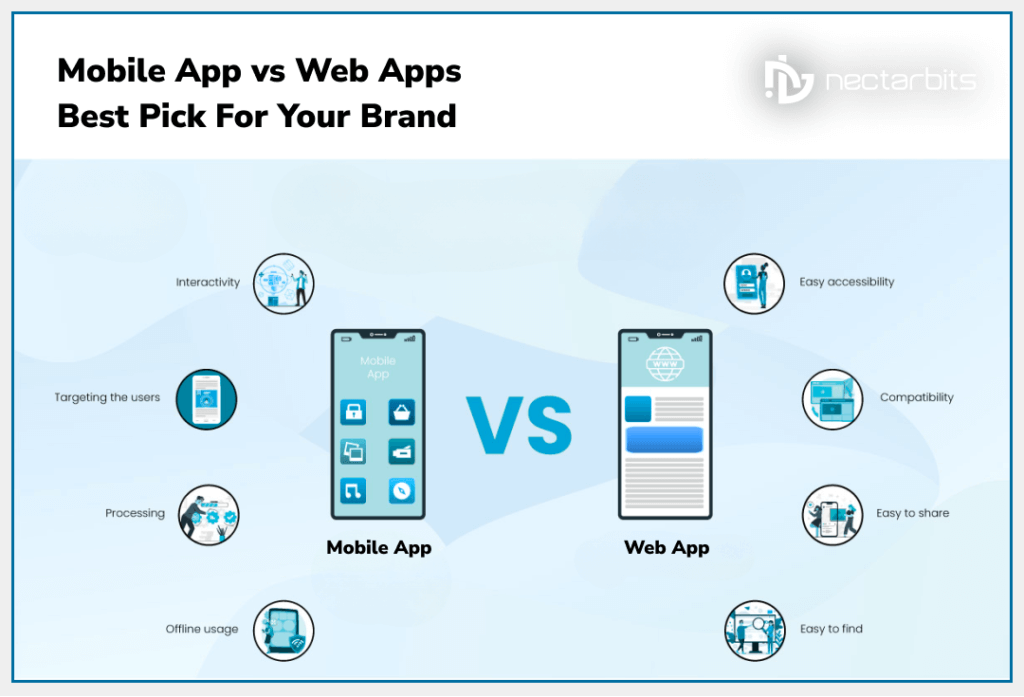
How is the Native App Better Than Web Apps?
1. Speed
The native apps are specifically built for one mobile device makes an app- automatically a great fit to the device and thus performs flawlessly after installation. For instance, when you buy and install an app from a Blackberry or iPhone application development company, it naturally turns into a piece of your handset. Propelling them on perfect handsets barely takes more than a couple of moments.
The web apps are internet-enabled apps which means the prerequisite is- a stable internet connection. When the consistent connection is unavailable, the users can’t access and use the app impeccably.
2. Cost Factor
From expert app designers to the average Joe, everyone speaks the same thing, that’s- the mobile application development cost for native apps is altogether higher than that of the web-based ones. The native applications that are perfect over a few stages, specifically are reasonably expensive because the developers need to invest double the time, effort, and dollars in the native app development as opposed to web app development. The average time and cost required to make models of native apps are likewise higher. On the off chance that you lean toward native applications, you’ll need to hold up additional costs!
3. Ease of Use
According to specialists from the best iPhone or Android Application Development Company, both native apps and web apps can be easy to understand – although the former appears to have the edge here. That’s because most native applications coordinate with the phone camera, sound/video recorder, and other handset features. Apps downloaded from mobile websites are not liable to have this feature.
4. App Store Approval
A noteworthy point is where web apps outscore native mobile applications. For an engineer who is into iPhone app development, it can take up to half a month, to get new applications approved and launched at the online app stores. And, after it’s all said and done, there is no certification that the app would gather adequate measures of clients’ advantage. On the other hand, web applications don’t require such store approval as they are accessible from the mobile device’s web browser and are thus, simpler to advance.
5. Security
Getting permeability on the app stores can be a somewhat time-expending process, and the technique works for native apps as well. People can rest assured that a mobile application, that has been protected by several OS layers, is quality-tested, and approved by the app store will be bug-free and entirely secure. No such affirmation is accessible for mobile web apps because there is no standardized quality control and no standardized SDKs and tools are used.
6. Prerequisite of inward memory
Native applications require a specific, pre-determined measure of memory space in handsets – to work proficiently. That’s why so much importance is given to choosing a mobile application development system that would not increase data transmission excessively on smartphones. As web apps don’t require any additional memory space to be propelled and worked, their comfort is unquestionably higher on this tally.
7. Finding the Essential Apps
With an array of web apps accessible, it can, at times turn out to be marginally precarious for clients to locate the ones that they require on their phones. There is no such thing with native mobile apps as the curated apps are listed and displayed on the Apple Play Store, Android Store, and the Blackberry App World. Choosing and downloading native apps is commonly considerably less unwieldy than scanning for reasonable web apps.
8. Maintenance
Native apps, by and large, require developers to write code separately for the apps built on different platforms. It comes with challenges- maintaining the app for various platforms, and the maintenance effort gets multiplied as the app is ported to more platforms. With web app maintenance, the scene is completely different. They are easier to maintain as a common codebase is used across multiple mobile browsers. The maintenance cost figures for web applications, naturally, are additionally lower.
9. Rendering the updates
The mobile apps need to be regularly upgraded with new features additions, modifications of existing ones, removing the undesired features, or improving UI/UX. When it comes to updating native apps, the apps need to be updated separately as unique coding is required for different platforms. Downloading the updates also requires users to update the apps. The web app update by the users is too easy as the latest version is always accessible.
Cost Comparison Between Native Applications and Web Applications
When considering Mobile Apps vs Web Apps, cost is a critical factor influencing the decision for businesses. While both app types have their unique benefits, the financial investment varies significantly based on factors like complexity, platform, and location of development teams. Here’s a Mobile vs Web App Development Guide with an estimated cost comparison based on geography.
| Geography | Native App Development Cost (USD) | Web App Development Cost (USD) |
| United States | $50,000 – $250,000 | $20,000 – $80,000 |
| United Kingdom | $40,000 – $200,000 | $15,000 – $60,000 |
| India | $10,000 – $50,000 | $5,000 – $20,000 |
Development costs in India, whether it be for native app development or web app development, are significantly lower than in other countries. If you are interested in learning more about how you can capitalize on such affordable rates for your next custom software development, you can learn more about Nectarbits.
Experience firsthand how their impeccable services have maintained their rank as one of the top software companies US and Canada for more than a decade.
Mobile Apps vs Web Apps Comparison: Key Cost Differences
Native App Development Costs:
Developing native apps for platforms such as iOS and Android takes their own time and makes development costs much higher. For businesses who want to be performance and quality-focused, native apps are the way to go providing a tailored user experience in mobile and web apps.
Web App Development Costs:
They are cheaper in terms of development, as web apps use a single code base. For those companies that have a limited budget for an app, this is great as it means you can have web apps and scale them as well as reach out to different devices.
Choosing the Right App Type for Your Business
This Mobile vs Web App Development Guide will not function without providing a better understanding of the difference between mobile apps and web applications. If you are an enterprise that is looking for the best app for business, take in mind the budget, the target audience, and the long-term scalability. Native apps possess perfection in terms of delivering a flashy and feature-rich experience, but web apps are favorable because of their low development cost and easy maintenance.
Ultimately, the best option: Your business needs will decide if your apps are mobile or web-based. This detailed comparison will help you choose what works best for your goals.
Conclusion: Who Wins the Tug of War?
At times, it tends to be hard to keep a tab on which version of a native app somebody is utilizing, which makes taking off redesign designs somewhat troublesome. As far as quality and execution, however, these native applications are superior to web apps. Everything considered native apps does appear to offer more client favorable circumstances – even though web apps additionally have a few positive purposes of their own.
We cannot declare a winner because both types of apps perform better than each other in different use cases. Decide your business app preferences, and then choose which one is the best fit for your business.
Pro Tip: If quality, reliability, security, and performance are your requirements, I suggest you move ahead with the native approach as no other development approach can out-rank native apps in these factors.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Mobile apps are platform-specific applications installed on devices, offering rich features and offline functionality. Web apps, on the other hand, run directly in web browsers, requiring no downloads and providing cross-platform compatibility.
– Mobile Apps:
– Installed on Android or iOS devices.
– Access to device features like camera and GPS.
– Offers offline usability.
– Web Apps:
– Runs on browsers using URLs.
– No device-specific installation is required.
– Requires a stable internet connection.
Web apps are generally more cost-effective than mobile apps because they require a single codebase to function across platforms, reducing development time and expenses.
– Mobile Apps:
– Higher costs due to separate development for iOS and Android.
– Better for feature-rich, performance-heavy apps.
– Web Apps:
– Single codebase reduces costs.
– Ideal for businesses with a limited budget.
Mobile apps usually deliver a superior user experience with seamless performance and access to device features, while web apps offer convenience with browser-based accessibility.
Mobile Apps:
– Smooth UI/UX optimized for specific devices.
– Leverages device hardware for enhanced interactivity.
Web Apps:
– Uniform UI across devices.
– Dependent on internet speed for performance.
The choice depends on business needs, target audience, and budget. Mobile apps are ideal for high-performance demands, while web apps suit wider accessibility goals.
– Mobile Apps:
– Best for businesses prioritizing user engagement and advanced features.
– Requires significant investment.
– Web Apps:
– Great for broader reach with lower costs.
– Easy maintenance with universal updates.
Yes, many businesses opt for both to cater to diverse audience needs and maximize their market presence.
– Benefits of Having Both:
– Mobile apps for personalized and feature-rich experiences.
– Web apps for easy accessibility and cost efficiency.