Quick Summary
Fuel costs silently drain fleet profitability when fuel usage isn’t visible in real time. This blog explains the IoT fuel tank monitoring benefits for large delivery fleets, showing how smart tank sensors bring end-to-end fuel visibility, prevent theft, optimize routes, reduce idling, and enable predictive maintenance, helping fleets cut fuel expenses by up to 30% before diving into the detailed analysis below.
In the competitive landscape of logistics and fleet management, fuel costs represent one of the most significant operational expenses, accounting for approximately 24-38% of total fleet operating costs according to the American Transportation Research Institute. For large delivery fleets managing hundreds or thousands of vehicles, even a small percentage reduction in fuel consumption translates to substantial annual savings. This is where IoT fuel tank monitoring benefits become game-changing for fleet operators seeking to maximize profitability while maintaining service excellence.
Traditional fuel management methods, manual tank readings, paper-based fuel logs, and periodic audits are increasingly inadequate in today’s data-driven logistics environment. These outdated approaches leave fleet managers blind to critical issues like fuel theft, inefficient routing, and vehicle idling that silently drain profits. IoT-enabled tank sensors are revolutionizing how large fleets monitor, manage, and optimize their fuel consumption, delivering measurable cost reductions backed by real-world data.
Understanding IoT Tank Sensors in Fleet Management
IoT tank sensors are sophisticated monitoring devices installed directly in vehicle fuel tanks that continuously track fuel levels, consumption patterns, and tank activities in real-time. These sensors leverage wireless connectivity to transmit data to centralized fleet management platforms, providing unprecedented visibility into fuel usage across entire fleet operations.
Unlike traditional dipstick measurements or manual fuel logs that capture snapshots at specific moments, IoT sensors provide continuous, automated monitoring. Modern IoT fuel monitoring systems utilize ultrasonic, capacitive, or pressure-based sensing technologies that deliver accuracy levels within 1-2% variance.
The fundamental architecture includes three key components: the physical sensor hardware installed in each vehicle tank, wireless communication protocols (typically cellular or LoRaWAN connectivity), and cloud-based analytics platforms that process and visualize the data. This infrastructure enables fleet managers to monitor fuel levels across hundreds of vehicles simultaneously from a single dashboard, receiving instant alerts for anomalies like sudden fuel drops, indicating potential theft or unusual consumption patterns suggesting maintenance issues.

The Hidden Costs Draining Fleet Profitability
Before examining how IoT sensors deliver savings, understanding the specific cost drains affecting large fleets provides essential context. Fleet managers face multiple fuel-related challenges that traditional monitoring methods fail to address effectively.
Fuel Theft and Pilferage
Fuel theft represents a massive hidden cost for fleet operations. Industry research estimates that fuel theft costs commercial fleet operations billions annually. For individual fleet operators, losses typically range from 2-5% of total fuel purchases, though some operations experience theft rates exceeding 10% without proper monitoring systems.
Fuel theft takes various forms: drivers siphoning fuel for personal vehicles, unauthorized fuel card usage, “phantom” fuel purchases where drivers claim refills that never occurred, and organized theft rings targeting fleet fuel supplies. Without real-time monitoring, these losses often go undetected for months or years.
Inefficient Route Planning
Poor route optimization directly impacts fuel consumption and operational costs. Research indicates that inefficient routing increases fuel consumption by 15-20% compared to optimized alternatives. For a 100-vehicle fleet averaging 15,000 miles annually per vehicle at 7 miles per gallon with diesel at $4.00 per gallon, inefficient routing could waste approximately $257,000-$343,000 annually.
Traditional routing approaches rely on driver experience and static planning that fails to account for real-time variables like traffic congestion, weather conditions, or delivery schedule changes. Modern logistics management solutions integrate real-time data to address these inefficiencies systematically.
Excessive Idling and Poor Driving Habits
Vehicle idling burns approximately 0.6-0.8 gallons of fuel per hour according to the U.S. Department of Energy, generating zero productive miles while contributing to maintenance costs through unnecessary engine wear. For fleet vehicles that idle an average of 1-2 hours daily, annual fuel waste per vehicle ranges from $2,400-$4,800 at current diesel prices.
Beyond idling, aggressive driving behaviors—rapid acceleration, harsh braking, excessive speeding—reduce fuel efficiency by 15-30%. A fleet of 250 vehicles with poor driving behavior controls could be wasting $450,000-$900,000 annually compared to implementing driver training and real-time monitoring systems.
Maintenance Issues and Fuel System Problems
Undetected maintenance problems significantly impact fuel efficiency. A vehicle with clogged air filters experiences 6-11% reduced fuel economy, while underinflated tires decrease efficiency by 0.2% per 1 PSI drop in pressure. Fuel system leaks, defective fuel injectors, and oxygen sensor failures create substantial waste that traditional inspection schedules often miss until problems become severe.
Poor maintenance practices increase operating costs by 8-12%, with fuel efficiency losses representing a substantial component. IoT monitoring enables predictive maintenance approaches that identify efficiency-degrading issues before they escalate into costly repairs or fuel waste.
Real Numbers: How IoT Tank Sensors Deliver Measurable Savings
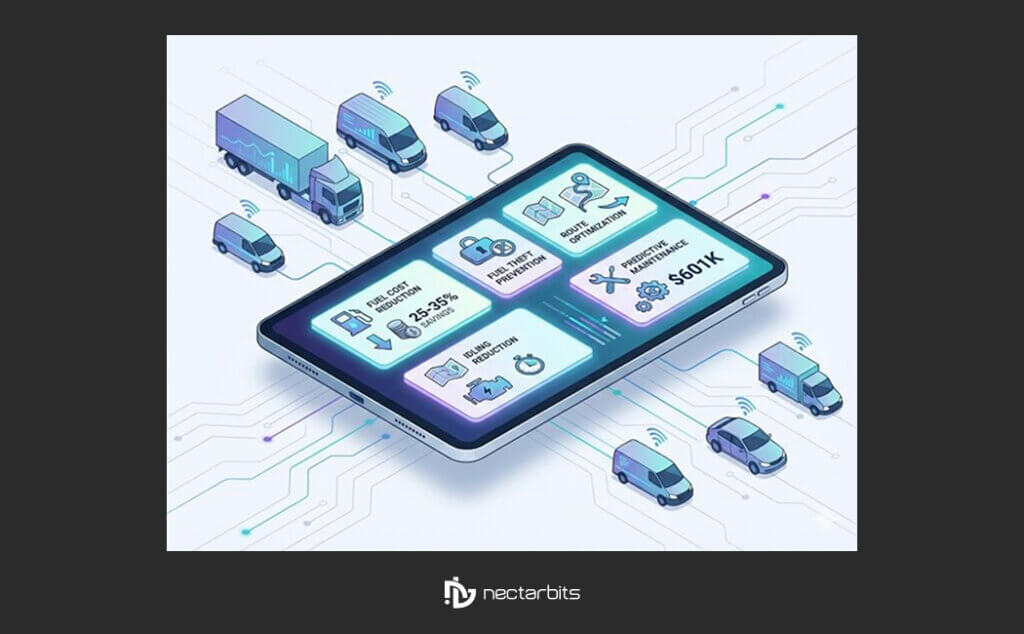
The transition from theoretical benefits to actual cost reduction requires examining real-world implementation data from fleets that have deployed IoT fuel monitoring systems. Multiple case studies and industry reports provide concrete evidence of the financial impact.
Fleet Fuel Cost Reduction with IoT: Industry Data
According to Verizon Connect’s Fleet Technology Report, fleets implementing comprehensive IoT fuel monitoring systems achieved average fuel cost reductions of 25-35% within the first year. This translates to substantial annual savings for large operations.
Consider a mid-sized delivery fleet with 200 vehicles, each averaging 25,000 miles annually at 8 miles per gallon fuel efficiency, with diesel priced at $3.85 per gallon:
- Baseline Annual Fuel Cost: 200 vehicles × 25,000 miles ÷ 8 mpg × $3.85 = $2,406,250
- After IoT Implementation (25% reduction): $2,406,250 × 0.75 = $1,804,687
- Annual Savings: $601,563
For larger operations managing 500+ vehicles, annual savings regularly exceed $1.5-2 million. These figures demonstrate that real-time fuel monitoring for delivery fleets delivers substantial ROI within the first year of operation.
Preventing Fuel Theft: Quantified Impact
Real-world implementations show dramatic theft reduction when IoT sensors are deployed. Before implementation, fleet operators typically estimate annual fuel theft losses at 2-5% of total fuel purchases based on discrepancies between fuel purchase records and odometer readings.
After deploying IoT tank sensors with real-time monitoring and automated alerts for suspicious fuel level drops, documented results show:
- Theft detection: 70-90% of theft incidents are identified within 24 hours
- Theft deterrence: 75-95% reduction in theft attempts within 12 months
- Financial recovery: For a 200-vehicle fleet spending $2.4 million annually on fuel, eliminating 4% theft losses saves $96,000 per year
The psychological deterrent effect proves as valuable as direct detection. When drivers know that every fuel transaction and tank level change is tracked and reviewed, theft attempts drop dramatically. This represents a significant component of IoT fleet management cost savings.
Optimizing Routes with Real-Time Fuel Data
Real-time fuel monitoring for delivery fleets enables dynamic route optimization based on actual consumption patterns rather than theoretical fuel economy ratings. This integration between fuel monitoring and route planning systems delivers measurable efficiency gains.
United Parcel Service (UPS) documented significant results from its route optimization system, which incorporates real-time fuel consumption data. The system reduced route miles by 100 million miles annually while cutting fuel consumption by 10 million gallons per year, generating savings exceeding $400 million.
While UPS represents an extraordinarily large operation, the principles scale to mid-sized fleets. Systems that integrate IoT fuel data with route optimization typically deliver 12-18% fuel savings through improved route efficiency.
For a 150-vehicle delivery fleet, route optimization integrated with IoT fuel monitoring generates approximately $270,000-$405,000 in annual fuel savings based on industry benchmarks.
Reducing Idling Through Behavior Monitoring
IoT fleet management cost savings extend significantly to idling reduction. Modern IoT sensor systems integrate fuel level monitoring with GPS tracking and engine diagnostics to identify excessive idling patterns across fleet operations.
Fleet operators implementing comprehensive IoT monitoring have documented specific idling reduction results:
- Average daily idling time reduced: From 80-90 minutes to 20-30 minutes per vehicle
- Annual fuel savings from idling reduction: $1,200-$1,500 per vehicle
- For 200-vehicle fleet: $240,000-$300,000 annual savings
These results come through a combination of automated engine shutdown protocols, driver coaching based on idling data, and establishing clear idling policies with measurable accountability. The system automatically generates weekly idling reports for each driver, with excessive idling triggering manager notifications and coaching interventions.
Predictive Maintenance Impact on Fuel Efficiency
IoT fuel monitoring systems reveal fuel efficiency degradation that signals developing maintenance issues before they escalate into major problems or breakdowns. This predictive maintenance capability generates both direct fuel savings and avoided breakdown costs.
A practical example: An IoT fuel monitoring system detects that a specific vehicle’s fuel economy has degraded from 8.2 mpg to 7.4 mpg over three weeks, a 9.8% decline. Immediate inspection reveals a developing fuel injector problem. Addressing this issue costs $450 in repairs, but prevents an estimated $2,800 in excess fuel consumption over the vehicle’s remaining months before scheduled maintenance would have caught the problem.
Multiplied across fleet operations, predictive maintenance enabled by IoT monitoring generates substantial savings. Fleet operators report fuel efficiency improvements of 8-12% after implementing predictive maintenance protocols.

IoT Tank Sensors vs. Traditional Fuel Management: Cost Comparison
Understanding the total cost of ownership for IoT fuel monitoring systems compared to traditional approaches provides essential context for investment decisions. The comparison must consider both direct costs and the operational efficiency differences.
| Cost Category | Traditional Management | IoT Monitoring System | Annual Difference (200 Vehicles) |
| Hardware/Installation | Minimal ($0-5,000) | $80,000-120,000 | -$80,000-115,000 (Year 1 only) |
| Monthly Service Fees | $0 | $20-40 per vehicle | -$48,000-96,000 |
| Labor for Manual Monitoring | $45,000-65,000 | $8,000-12,000 | +$33,000-57,000 |
| Fuel Theft Losses | $48,000-120,000 (2-5%) | $2,400-12,000 (0.1-0.5%) | +$36,000-118,000 |
| Inefficient Routing Costs | $257,000-$343,000 | $90,000-$137,000 | +$120,000-$253,000 |
| Idling Waste | $240,000-$480,000 | $48,000-$96,000 | +$144,000-$384,000 |
| Maintenance Inefficiency | $58,000-$96,000 | $12,000-$29,000 | +$29,000-$84,000 |
| Total Annual Costs | $648,000-1,109,000 | $260,400-$502,000 | +$362,000-$685,000 |
This comparison demonstrates that despite the upfront investment and ongoing subscription costs, IoT fuel monitoring systems deliver net positive returns within the first year of operation for most medium to large fleets. The ROI calculation becomes even more favorable in subsequent years when initial hardware costs are fully amortized.
Implementing IoT Fuel Monitoring: A Practical Roadmap
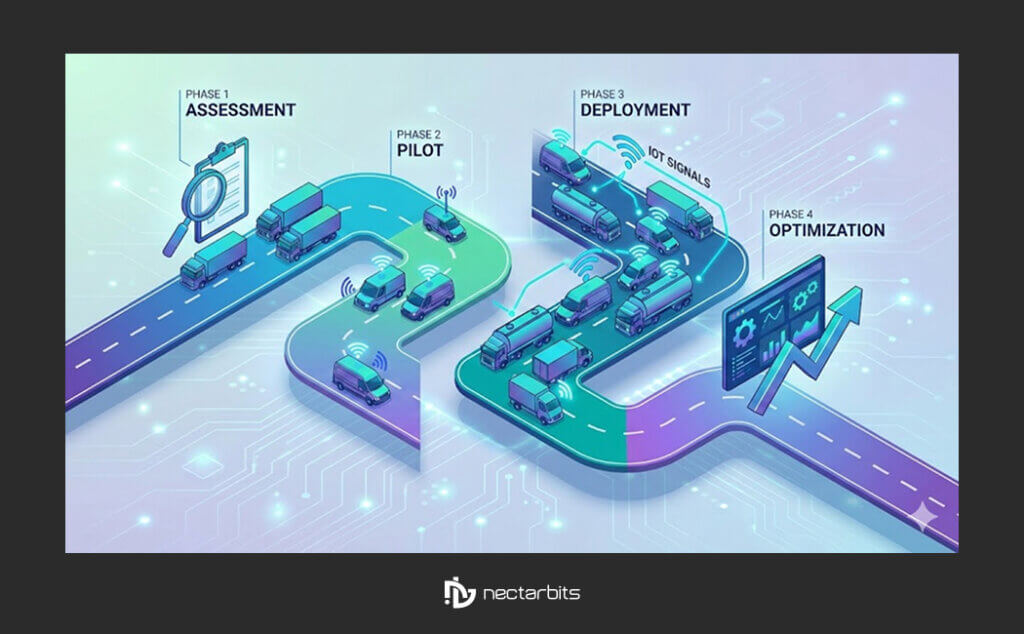
Successfully deploying IoT tank sensors across large fleet operations requires structured planning and phased implementation. Organizations that follow systematic rollout processes achieve faster ROI and higher adoption rates compared to rushed deployments.
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Weeks 1-4)
Begin with comprehensive baseline data collection on current fuel consumption, costs, and suspected problem areas. Conduct a thorough audit of existing fuel management practices, interview drivers and fleet managers about challenges, and analyze historical fuel purchase records to identify patterns.
Establish clear, measurable objectives for the IoT implementation. Rather than vague goals like “reduce fuel costs,” specify targets such as “reduce fuel theft to below 0.5% of purchases,” “decrease average vehicle idling to under 30 minutes daily,” and “improve fleet fuel efficiency by 15% within 12 months.”
Select appropriate IoT sensor technology based on your fleet composition, operational environment, and budget constraints. Consider factors including sensor accuracy specifications, wireless connectivity requirements, battery life for wireless sensors, compatibility with your vehicle tank types, and integration capabilities with existing fleet management systems. Working with custom software development experts ensures your IoT implementation integrates seamlessly with existing operational systems and business processes.
Phase 2: Pilot Program (Months 2-4)
Rather than fleet-wide deployment, implement a pilot program with 10-15% of your vehicles representing diverse use cases (long-haul routes, urban delivery, different vehicle types). This controlled pilot enables you to identify integration challenges, refine data analysis processes, and demonstrate ROI before committing to full deployment.
During the pilot, closely monitor system performance, data accuracy, and user adoption challenges. Gather feedback from drivers and managers about the interface usability, alert relevance, and reporting usefulness. This feedback period allows you to optimize configurations before expanding to the full fleet.
Document specific cost savings achieved during the pilot phase. Quantify fuel theft reduction, idling improvements, maintenance issues detected early, and efficiency gains from route optimization. This documented ROI justifies the broader investment and builds organizational support for full deployment.
Phase 3: Full Fleet Rollout (Months 5-10)
Execute staged deployment across the remaining fleet, typically organized by region, vehicle type, or operational division. Staged rollout prevents overwhelming installation resources and allows you to apply lessons learned from earlier deployment phases.
Implement comprehensive training programs for all stakeholders: drivers need to understand how their behavior is monitored and the expectations for fuel management, fleet managers require training on data interpretation and alert response protocols, and maintenance teams must learn how to utilize fuel efficiency data for predictive maintenance decisions.
Establish clear policies and accountability structures based on the IoT data. Define acceptable idling thresholds, fuel consumption benchmarks for different route types, and investigation protocols for fuel anomalies. Communicate these policies transparently while emphasizing that monitoring aims to support driver performance rather than punitive oversight.
Phase 4: Optimization and Continuous Improvement (Ongoing)
After full deployment, focus on continuous optimization of fuel management practices based on accumulated data insights. Regularly review performance metrics against baseline and target goals, identify new opportunities for efficiency improvements, and refine route planning and maintenance scheduling based on consumption patterns.
The woes of inventory mismanagement are deepening with the traditional approach to fleet fuel management. Here, an IoT-enabled inventory system enhances system responsiveness, improves operational efficiency, and facilitates cost control through data-driven decision-making that evolves as operational patterns change.
Advanced Integration: Fuel Delivery and IoT Monitoring
For operations that manage their own fuel inventory or coordinate with delivery solutions, IoT tank sensors provide critical real-time data. The future of the fuel delivery app is an IoT-enabled smart meter that communicates directly with delivery systems. Companies can explore successful fuel delivery apps to understand market trends in automated fuel ordering and just-in-time delivery.
This integration enables several key capabilities—automated reordering triggers when tank levels reach predetermined thresholds, eliminating manual monitoring and preventing costly stockouts. Optimized delivery scheduling based on consumption patterns reduces emergency deliveries that incur premium costs. Better inventory management across distributed fleet locations ensures fuel availability while minimizing carrying costs.
Modern on-demand fuel delivery app solutions seamlessly connect with IoT monitoring systems to provide real-time fuel management. These platforms automatically trigger orders when sensors detect fuel levels falling below predetermined thresholds, schedule deliveries during optimal time windows to avoid operational disruptions, and provide complete visibility into fuel consumption patterns across the entire fleet.
Professional fuel delivery app development creates seamless connections between IoT sensors and ordering systems, enabling just-in-time fuel management that reduces working capital requirements while ensuring operational continuity.
Leveraging Technology for Comprehensive Fleet Solutions
Modern fleet management requires integrated technology platforms that connect various operational systems. mobile app development enables managers to access real-time fuel data from anywhere, receive instant alerts about anomalies, and review driver performance metrics on-demand.
These mobile solutions provide drivers with immediate feedback on their fuel consumption patterns, helping them adjust their behaviors in real-time rather than waiting for weekly or monthly performance reviews. This immediate feedback loop accelerates behavior change and drives faster improvements in fuel efficiency.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Despite clear ROI evidence, fleet operators face several challenges when implementing IoT fuel monitoring systems. Understanding these obstacles and mitigation strategies increases implementation success rates.
Driver Resistance and Privacy Concerns
Drivers sometimes perceive comprehensive monitoring as intrusive surveillance that signals mistrust. This perception can damage morale and create resistance that undermines system effectiveness. Successful implementations address these concerns through transparent communication about monitoring purposes, demonstrating how data improves working conditions through better route planning and faster issue resolution.
Emphasize that monitoring targets system optimization rather than punitive oversight. Share aggregated performance data that shows fleet-wide improvements without singling out individual drivers for criticism. Recognition programs that reward fuel-efficient driving based on objective IoT data can transform monitoring from a negative into a positive motivator.
Technical Integration Complexity
Legacy fleet management systems may lack modern API capabilities for seamless IoT integration. Data format incompatibilities and connection protocol mismatches create integration headaches that delay ROI realization.
Working with experienced implementation partners who understand both IoT sensor technologies and fleet management systems bridges these technical gaps. Allocate sufficient time and resources for integration testing before full deployment, and maintain close collaboration between your IT team, the IoT sensor provider, and your fleet management software vendor throughout implementation.
Upfront Investment Justification
Finance departments may resist the significant upfront investment required for comprehensive IoT deployment. Build compelling business cases by presenting documented case studies from similar fleet operations, calculating specific ROI based on your fleet’s current fuel costs and identified inefficiencies, and proposing pilot programs that demonstrate value before full commitment.
The data presented in this article provides concrete evidence that properly implemented IoT fuel monitoring systems deliver measurable, substantial returns that justify the investment for most medium to large-sized fleet operations.
The Future of IoT in Fleet Fuel Management
IoT tank sensor technology continues evolving rapidly, with emerging capabilities promising even greater cost reduction potential for fleet operators willing to adopt cutting-edge solutions.
Next-generation systems will move beyond monitoring and reporting to autonomous optimization, automatically adjusting route assignments based on real-time fuel consumption patterns, triggering maintenance interventions when fuel efficiency degradation exceeds acceptable thresholds, and dynamically rebalancing fuel inventory across distributed fleet operations without human intervention.
As fleets increasingly adopt electric, hydrogen, and other alternative fuel vehicles, IoT monitoring will evolve to optimize energy consumption across mixed-fuel fleets. Systems will recommend optimal charging strategies for electric vehicles, manage hydrogen refueling timing and location, and coordinate traditional and alternative fuel resources for maximum cost efficiency.
Future IoT systems will integrate real-time fuel price monitoring across geographic regions according to the IoT Fleet Management Market Forecast – Industry Research, automatically recommending optimal refueling locations and timing based on price forecasts. This dynamic optimization could save large fleets an additional 3–7% on fuel purchases, as IoT fleet management platforms increasingly combine real-time data, predictive analytics, and fuel management intelligence to reduce operating costs

Ready to Cut Your Fleet Fuel Costs with IoT Monitoring?
The evidence is clear: IoT fuel tank monitoring benefits deliver substantial, measurable cost reductions for large delivery fleets. From preventing theft to optimizing routes, reducing idling, and enabling predictive maintenance, these systems transform fuel management from a cost center into a competitive advantage.
For fleet operations spending $2-5 million annually on fuel, implementing comprehensive IoT monitoring typically generates $500,000-$1.5 million in annual savings—a compelling ROI that justifies the investment within months rather than years.
Explore Related Topics
For operations seeking comprehensive efficiency improvements beyond fuel management, discover how cutting fuel costs through route optimization can complement your IoT monitoring initiatives for maximum savings.
FAQs:-
Modern IoT fuel tank sensors use ultrasonic, capacitive, or pressure-based technologies and typically deliver 98–99% accuracy. In real fleet deployments, this level of precision is enough to clearly detect fuel theft, abnormal consumption, refueling events, and gradual fuel loss caused by leaks or maintenance issues.
Yes. Fleets using IoT fuel tank monitoring report 70–95% reduction in fuel theft within the first year. Real-time alerts are triggered when sudden fuel drops occur while the vehicle is stationary or outside authorized zones, allowing managers to act immediately rather than discovering losses weeks later through manual audits.
Based on industry reports and fleet case studies, large fleets typically achieve 25–35% fuel cost reduction after implementing IoT fuel tank monitoring. Savings come from theft prevention, route optimization, reduced idling, improved driving behavior, and early detection of fuel-efficiency-related maintenance issues.
Most modern IoT fuel monitoring systems are built with APIs and cloud-based dashboards, allowing seamless integration with GPS tracking, route optimization, ERP systems, and fuel delivery platforms. This integration enables data-driven decisions such as dynamic route planning and automated fuel replenishment.
While large fleets see the fastest ROI, mid-sized fleets (50–100 vehicles) also benefit significantly. Even smaller fleets recover costs quickly by eliminating fuel theft and reducing idle time. Most providers offer scalable pricing models, making IoT fuel tank monitoring practical beyond enterprise-level operations.








